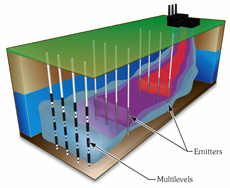
Enhanced Aerobic Bioremediation And The Waterloo Emitter™
With the help of our Model 703 Waterloo Emitter Operating Principles video series, let’s review how the Waterloo Emitter works, some tips for application, and the advantages it provides to remediation professionals. The Waterloo Emitter has been shown to be very effective at cleaning up sites contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons, so let’s focus… Continue Reading »