What is a Multilevel System?
Depth Discrete Groundwater Monitoring
Reduce Costs and Field Time
Isolate and Monitor Discrete Zones
High Resolution Monitoring:
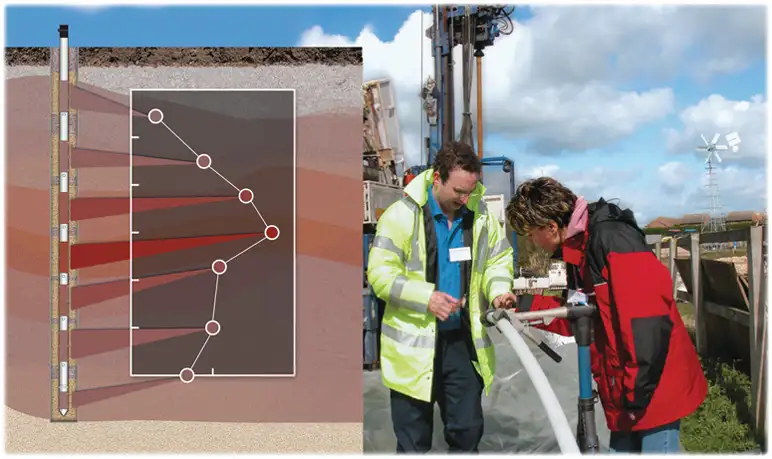
Get the real picture
Detailed Vertical Profiles:
Accurate concentration levels

Introduction
A multilevel system is a groundwater instrument, which allows the monitoring of a number of discrete groundwater zones within a single borehole. The system typically consists of seals and ports, which are placed at varying depths along a casing string, effectively isolating and providing access to each monitoring interval.
Evolution of the Technology
Due to numerous benefits associated with multilevel monitoring systems, more consultants and site managers are considering them a suitable option for groundwater investigations. Previously, multilevel systems were often restricted to higher profile projects where a greater level of understanding of contaminant plume migration and groundwater flow regimes was required.
In addition, they were viewed as being more costly and limited to bedrock applications.
In reality, multilevel monitoring devices can be designed to suit a much wider range of projects and save money not only on long-term monitoring costs, but also through increased accuracy in identifying contaminated zones and concentrations.
Initially, multilevel systems were created to allow delineation of contaminated groundwater in fractured bedrock (Cherry and Johnson, 1982) with the earliest systems designed for sample collection rather than full scale monitoring, including sampling, level measurements and permeability testing. Prior to advancements in multilevel instrument design this detailed monitoring was accomplished either by drilling numerous separate boreholes to various depths, often referred to as a cluster type installation, or by installing a series of piezometers at different depths in a single borehole, nested type. The single hole, nested type piezometers were introduced to limit costs and disturbance to the aquifer; however, uncertain seal placement resulting in possible interconnection between monitoring zones resulted in the EPA (1986) stating that “Information obtained on multiple piezometer placement in a single borehole may generate erroneous data”. Cluster type installations, subsequently, became the more popular approach. Today’s multilevel monitoring installations are continually increasing in reliability, with improvements in the integrity of seals. Their flexibility has made them a viable option for the majority of projects involving groundwater monitoring.
Benefits of Using Multilevel Systems
- Depth-discrete data provides site assessors with a better understanding of the 3D groundwater flow and distribution of contaminants.
- Ideal for monitoring of natural attenuation or remediation processes.
- More accurate risk assessments.
- Minimizes risk of additional contaminant pathways.
- Vertical hydraulic head data for model calibration.
- Reduced long-term monitoring costs.
Collecting Samples and Measuring Water Levels
Solinst Water samples can be collected using sampling devices like peristaltic pumps, pneumatic pumps or inertial pumps. The depth to water can be measured in each zone with small diameter water-level tapes or transducers. The small diameter pressure transducers allow for automated level monitoring, facilitating continuous monitoring of water levels during hydraulic tests, or long-term monitoring. It is often possible to install double valve or bladder pumps and pressure transducers at each zone of the system to maximize the information gathered from each sampling zone.
Multilevel Systems

